- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录181 > 2938840 (Phoenix Contact)POWER SUPPLY 1A 24VDC
�� �
�
 �
�Basics�
�2.4.2�
�Forward� Converter�
�Primary� switched-mode� power� supply� units� with� an� output� power� of� greater� than� 200� W�
�used� to� be� designed� with� forward� converters.� Today,� flyback� converters� may� be� used� for�
�an� output� power� of� up� to� 1000� W.� Therefore,� forward� converters� are� more� and� more� being�
�replaced� by� space-saving� and� reliable� flyback� converters,� also� for� higher� performance�
�ranges.� The� following� section� explains� the� circuit� principle� of� forward� converters.�
�The� major� difference� between� a� flyback� converter� and� a� forward� converter� is� that� in� the�
�forward� converter� the� energy� transport� from� the� primary� to� the� secondary� circuit� is� carried�
�out� with� the� switch� closed.� The� forward� converter� owes� its� name� to� this� principle.�
�The� design� of� the� forward� converter� is� more� complicated� than� the� design� of� the� flyback�
�converter.� The� transformer� requires� an� additional� primary� winding� and� the� output� circuit�
�additional� diodes� and� an� inductance.� This� makes� forward� converters� larger� in� size� and�
�heavier� than� flyback� converters.�
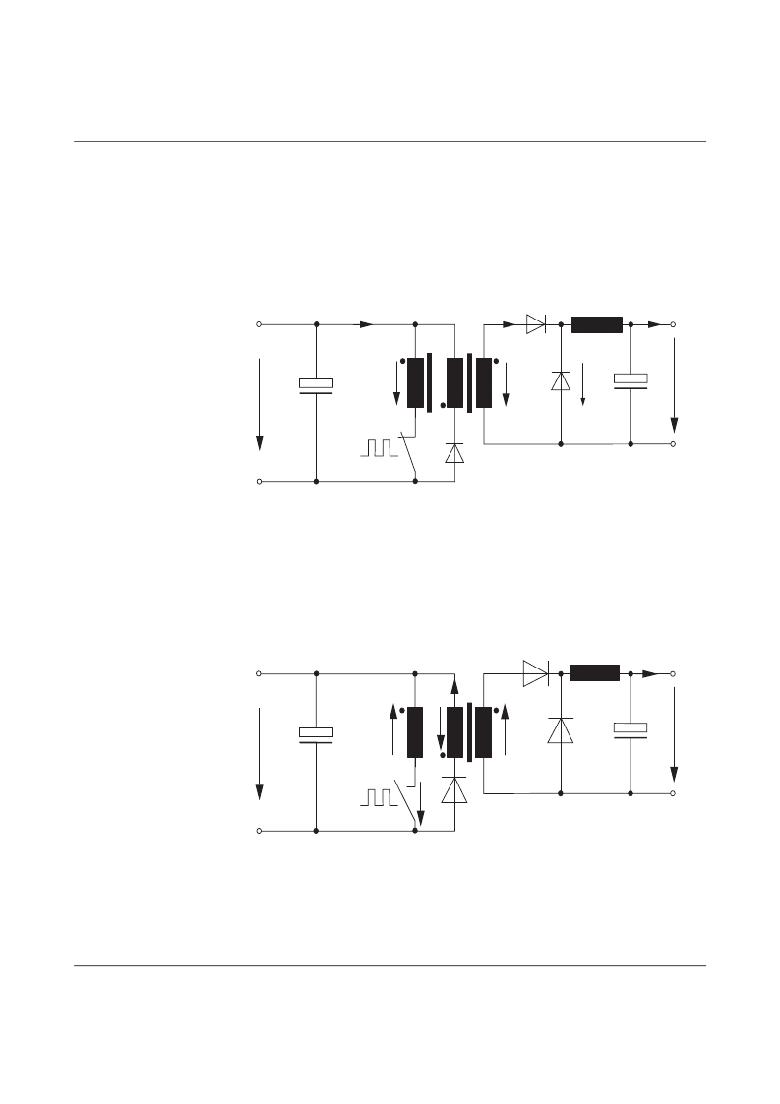
�Method� of� Operation�
��The� power� switch� S1� is� switched� on� and� off� by� means� of� a� controller� with� the� control�
�voltage� U� ctrl� .� The� value� of� the� output� voltage� U� out� depends� on� the� pulse� duty� factor� of�
�switch� S1.� The� value� of� the� output� voltage� U� out� is� continuously� measured� and� transmitted�
�to� the� controller.� In� this� way,� a� stabilized� output� voltage� U� out� is� generated.�
�Energy� transport� in� the� forward� converter� is� carried� out� in� two� steps.� For� easier�
�understanding,� the� procedures� are� illustrated� in� two� different� graphics.�
�Figure� 2-16� shows� the� circuit� with� switch� S1� closed.� During� this� operating� cycle� energy� is�
�taken� from� the� supplying� network� and� transformed� into� the� output� circuit.�
�Figure� 2-17� shows� the� circuit� with� the� switch� opened.� In� this� operating� cycle� no� energy� is�
�transformed� into� the� secondary� circuit.� Storage� inductance� L1� avoids� interruptions� of� the�
�energy� flow� in� the� secondary� circuit.�
�The� corresponding� characteristic� curves� of� the� voltage� and� current� are� shown� in�
��5598_en_03�
�PHOENIX� CONTACT�
�2-19�
�发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
2938853
DIN RAIL POWER SUPPLY 24VDC 5A
2938866
POWER SUPPLY 10A 24VDC
2938879
POWER SUPPLY 40A 100-240AC 24DC
2938976
POWER SUPPLY 20A 100-240AC 48DC
299D225X0025AB1
CAP TANT 2.2UF 25V 20% RADIAL
2AC109
SWITCH DOOR ROD SPDT 15A SCREW
2AC110
SWITCH DOOR ROD SPDT 15A QC
2AC19
SWITCH DOOR ROD SPDT 15A SCREW
相关代理商/技术参数
2938853
功能描述:DIN导轨式电源 QUINT 24VOLT 5AMP
RoHS:否 制造商:Mean Well 产品:Linear Supplies 商用/医用:Commercial 输出功率额定值:960 W 输入电压:180 VAC to 264 VAC, 254 VDC to 370 VDC 输出端数量:1 输出电压(通道 1):48 V 输出电流(通道 1): 输出电压(通道 2): 输出电流(通道 2): 输出电压(通道 3): 输出电流(通道 3): 尺寸:150 mm L x 110 mm W
2938860-2
制造商: 功能描述: 制造商:undefined 功能描述:
2938866
功能描述:DIN导轨式电源 QUINT100-240AC/24DC 24VDC 10A
RoHS:否 制造商:Mean Well 产品:Linear Supplies 商用/医用:Commercial 输出功率额定值:960 W 输入电压:180 VAC to 264 VAC, 254 VDC to 370 VDC 输出端数量:1 输出电压(通道 1):48 V 输出电流(通道 1): 输出电压(通道 2): 输出电流(通道 2): 输出电压(通道 3): 输出电流(通道 3): 尺寸:150 mm L x 110 mm W
2938879
功能描述:DIN导轨式电源 QUINT 24VOLT 40AMP RoHS:否 制造商:Mean Well 产品:Linear Supplies 商用/医用:Commercial 输出功率额定值:960 W 输入电压:180 VAC to 264 VAC, 254 VDC to 370 VDC 输出端数量:1 输出电压(通道 1):48 V 输出电流(通道 1): 输出电压(通道 2): 输出电流(通道 2): 输出电压(通道 3): 输出电流(通道 3): 尺寸:150 mm L x 110 mm W
2938905
制造商:Phoenix Contact 功能描述:Primary Switched-Mode Power Supply
2938918
功能描述:DIN导轨式电源 100-240AC 5DC 4A RoHS:否 制造商:Mean Well 产品:Linear Supplies 商用/医用:Commercial 输出功率额定值:960 W 输入电压:180 VAC to 264 VAC, 254 VDC to 370 VDC 输出端数量:1 输出电压(通道 1):48 V 输出电流(通道 1): 输出电压(通道 2): 输出电流(通道 2): 输出电压(通道 3): 输出电流(通道 3): 尺寸:150 mm L x 110 mm W
2938921
功能描述:DIN导轨式电源 100-240AC 12DC 3A RoHS:否 制造商:Mean Well 产品:Linear Supplies 商用/医用:Commercial 输出功率额定值:960 W 输入电压:180 VAC to 264 VAC, 254 VDC to 370 VDC 输出端数量:1 输出电压(通道 1):48 V 输出电流(通道 1): 输出电压(通道 2): 输出电流(通道 2): 输出电压(通道 3): 输出电流(通道 3): 尺寸:150 mm L x 110 mm W
293893-000
制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:RD16A20-31-S9-00